The computing system is one of the technologies redefining the way we work and play. In addition to reducing the company’s IT infrastructure headache, the powerful computing framework ensures smarter, faster, and more productive business operations. Also, powerful computing systems help small businesses leverage cutting-edge technology at an affordable price. It is crucial for a business to choose the right computing system. However, choosing the right computing system for the smooth functioning of an organization is a tedious task. Knowing the distinctions between different computing systems, including Fog Computing vs cloud Computing vs edge Computing, can help tremendously.
In this post, we will walk you through the key differences between three major computing systems: fog, cloud, and edge. Read this post to gather all the information that you need to have before choosing a computing system. The following insight will help you make a well-informed decision. Let’s dive in…
First off, let’s understand the basics of these computing frameworks. Here we go…
Table of Contents
- Understanding Different Computing Models
- What Is Fog Computing?
- What Is Cloud Computing?
- What Is Edge Computing?
- Critical Differences Among Fog Computing Vs Cloud Computing Vs Edge Computing
- Location of Data Processing
- Purpose
- Processing Power and Storage Capacities
- Data Distribution
- Latency Issues
- Scalability
- Redundancy
- Economic Considerations
- Practical Applications
- Fog Computing Vs Cloud Computing Vs Edge Computing: Which is Better?
Understanding Different Computing Models
What Is Fog Computing?
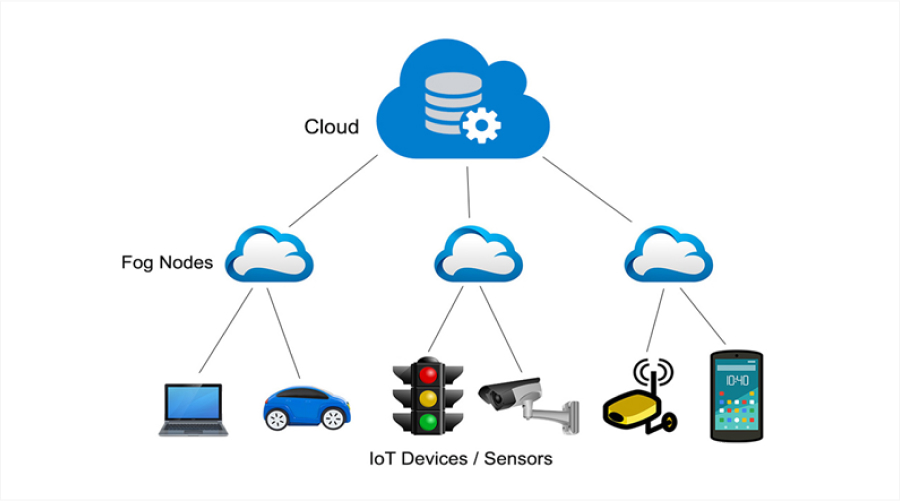
Fog computing, also known as fogging, is one of the popular computing frameworks that helps businesses process data and store information. This is a decentralized computing architecture that delivers the strength and benefits of cloud computing capabilities right to the location where the data is generated. Fog computing aims to enhance efficiency, improve safety considerations, and minimize latency issues. Take a look at the pros and cons of Fogging in computing…
Pros of Fog Computing
- Reduces the amount of data sent to the cloud storage system
- Saves the cost and consumption of network bandwidth
- Improves the responsiveness by reducing latency
- Ensures the end-to-end security of the data to protect it from malicious crooks
- Adds layers of security to boost the confidence of diverse industries
Cons of Fog Computing
- High traffic increases the chances of traffic congestion and reduced connectivity
- Due to the extra layer between the host and the cloud, the performance is compromised
- It makes data management a tedious task
- Vulnerable to Man in the Middle attacks or Internet Protocol address spoofing
- Costly due to additional hardware costs
What Is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing refers to distribution of computing services over the internet, or “the cloud.” It is a one-stop destination for IT resources that follows an on-demand pay-per-pricing policy. It allows users to access computing resources on-demand, such as storage, databases, servers, networking, software, and analytics. In contrast to the traditional IT structure, it offers businesses and customers greater flexibility and scalability. Because of its high responsiveness and accessibility, it is an indispensable cutting-edge technology in business settings. It benefits all kinds of businesses, from startups to global organizations. Read ahead for its pros and cons…
Pros of Cloud Computing
- Faster and smarter solution
- Used for innovation and redesigning purposes due to its high–responding nature
- Highly scalable and can adjust according to business-changing demands
- Pay for the IT resources your team uses
- Expand business globally with its global network services
- Aids diverse industries attain a competitive edge
Cons of Cloud Computing
Vulnerable to service outages and downtime
Security and privacy issues
Limited control and flexibility; owned and monitored by the cloud service provider
No easy switching between cloud services; the problem of vendor lock-in persists
Expensive for small-scale industries and start-ups
What Is Edge Computing?
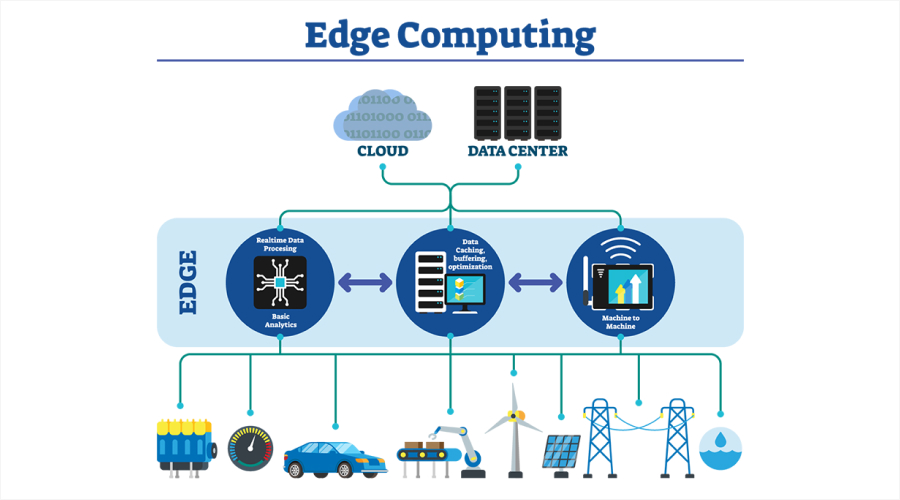
Edge computing is a distributed computing architecture that brings computing power nearer to the origin of data generation and processing. This facilitates quicker processing and immediate insights, while minimizing bandwidth consumption and enhancing application performance. Also, it allows you to do faster data analysis, foster opportunities for enhanced business growth, and refine customer preferences. Due to its exceptional performance, both small-scale and global enterprises consider it an effective cutting-edge computing solution. Take a look at its pros and cons…
Pros of Edge Computing
- Minimizes network bandwidth and server resources
- A cost-effective computing solution
- Reduces latency
- Improves application performance
- Helps in faster data analysis
- Comes with multiple functionalities
Cons of Edge Computing
- Additional local hardware is necessary for its optimal functioning
- Limited processing power
- Trouble communicating with the edge nodes and the cloud
- Data management challenges
- Complex architecture
- Higher cost
Let’s now take a look at the key differences between these three robust computing systems. Here we go…
Critical Differences Among Fog Computing Vs Cloud Computing Vs Edge Computing
Here are the key distinctions between Fog Computing vs. cloud Computing Vs. Edge Computing based on different criteria. Knowing these differences can help you greatly. Take a look…
1. Location of Data Processing
Understanding the location of data processing is crucial because of numerous reasons. It ensures data availability, accessibility, security, and network performance. Let’s know the difference between fog, cloud, and edge computing solutions based on the location of data processing. Take a look…
Fog Computing
Unlike other advanced computing solutions, data processing in Fog computing is done locally on the network’s edge services. It is not sent to a central location for processing. The outcome is improved performance and reduced latency.
Cloud Computing
In cloud computation, data processing is done on a central cloud server. The user needs to choose paid cloud computing services, such as Amazon Web Services, Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure, Oracle Cloud, IBM Cloud, etc., for data processing.
Edge Computing
The data processing for edge computing occurs at the network’s edge, either on the computer system or a local server. This improves network performance, customer satisfaction, and data processing in real-time.
2. Purpose
Computing solutions bring major differences to the organization where the advanced solution is integrated. Let’s understand the difference between Fog Computing Vs. Cloud Computing Vs. Edge Computing based on the purpose they are designed to meet. Here we go…
Fog Computing
Fog computing is ideal for real-time data processing and decision-making in diverse sectors, such as retail, autonomous vehicles, and industrial automation. It can efficiently process data from sensors. This efficiently predicts a proactive approach to maintenance.
Cloud Computing
The scope of cloud computing is wider than fog computing and edge computing. It ensures faster disaster recovery, comprehensive data backup, and business growth. One of the key aspects of cloud computing solutions is their significantly lower cost compared to other advanced computing options.
Edge Computing
Very often, power and utility companies integrate the IoT sensors and functionalities of edge computing to enhance their IT infrastructure’s performance. It improves efficiency, simplifies maintenance, reduces downtime, and automates the power grid. Also, it reduces network connectivity issues at remote locations.
3. Processing Power and Storage Capacities
Knowing processing power and storage capacities is crucial when it comes to choosing computing services. Having knowledge of the processing power and storage capacities of different computing systems helps you make an informed decision. Go over the following discussion to understand the difference between Fog, Cloud, and Edge computing based on their efficiency and performance. Read on!
Fog Computing
The processing power and storage capacities of fog computing are limited. This is because it largely depends on the local networks. It is not connected to the centralized data server for limitless functioning.
Cloud Computing
In contrast to fog computing and edge computing, cloud computing offers limitless data processing and storage capacities. It can handle multiple tasks and operate various functions simultaneously.
Edge Computing
Like fog computing, edge computing also offers limited processing power and storage capacities. Many times, data management becomes critical with its integration. It truly needs more development with optimization techniques and AI algorithms.
4. Data Distribution
Again, when it comes to choosing between Fog computing, Cloud computing, and Edge computing, knowing how they distribute data is crucial to making an informed decision. Let’s understand the following description to know their different data distribution procedures and their impacts:
Fog Computing
Data manipulation is difficult in fog computing because data remains distributed among nodes only. Therefore, it ensures higher data security and minimal downtime compared to cloud computing.
Cloud Computing
The downtime is more in cloud computing because everything is stored in one place, and if anything goes wrong anywhere, it can negatively impact the entire system. Furthermore, data vulnerability is more common in cloud computing than in other systems.
Edge Computing
Edge computing is a more preferable option out of the three. This is because of its robust data security network. The data is stored directly on the device. It is not distributed.
5. Latency Issues
Latency often interferes with the performance of a computing service. Frequent or prolonged latency can significantly hinder a business’ progress in the process. Take a look at the following discussion to learn the difference between these three computing systems based on latency issues.
Fog Computing
Fog computing is more successful than cloud computing in processing data in real time. This factor makes it suitable for latency-sensitive devices.
Cloud Computing
Conversely, latency issues are more common in cloud computing. This is because data has to travel back and forth to the central data center. This makes it an unsuitable choice for devices that take time to process.
Edge Computing
Edge computing is ideal for devices that require quick processing action. It reduces latency to a large extent.
6. Scalability
Scalability refers to the adaptability of the computing services. Take a look at the following discussion to understand how scalability differs in these three computing services. Read on…
Fog Computing
Fog computing is less scalable than cloud computing. However, it allows additional resources and services to be added to the edge network.
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is one of the most scalable computing services. It can handle a large database, processing, and storage requirements. Furthermore, it is highly adaptable to the changed business settings.
Edge Computing
Edge computing has limited powers when it comes to scalability. However, it is considered useful for remote locations or distributed operations.
7. Redundancy
Redundancy refers to having multiple copies to retrieve data in case it is lost. Let’s find out the difference between Fog, Cloud, and Edge computing based on redundancy. Here we go…
Fog Computing
Fog computing provides redundancy by distributing services and resources. It ensures data processing can continue even if services fail.
Cloud Computing
Like fog computing, cloud computing ensures data redundancy to reduce the impact of the system outage. It does not store all the data in one place and helps you prepare to keep business operations running smoothly.
Edge Computing
Edge computing also provides redundancy to address the future challenges of accidental data loss or service outage.
8. Economic Considerations
Now that you have explored key differences between them based on various factors. Let’s understand how the cost of these three computing solutions sets them apart. Here we go…
Fog Computing
Fog computing is more focused on personalized customer experience. It is usually established from the ground up or through a blend of existing computational technology. It likely comes with a higher price tag than edge computing.
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing cost varies by network needs, IT resources, and storage capacity. According to a data source, most enterprises with 1000 employees spend $2.4m- $6m annually. Although the leading vendors, such as Microsoft and Amazon, provide cloud computing, enterprises can negotiate prices by opting for customizable services. These providers have a fixed and recurring fee structure.
Edge Computing
Like cloud computing, organizations purchase edge computing services from vendors such as Dell, Amazon, and Microsoft. They can set up their own Edge infrastructure for optimal results. Depending on the usage and the quality of IT resources, it is more economical than the fog computing service.
9. Practical Applications
Even with the progress of Edge and Fog computing services, cloud computing continues to be the most favored option by businesses. Businesses that have relied on computational needs for years cannot substitute their computing requirements with Edge and Fog computations. Go over the following insight to understand the differences between three based on their applications. Read on…
Fog Computing
Fog computing is beneficial for industries that require data processing more quickly. This computing service is pretty popular in the healthcare sector, industrial automation, autonomous vehicles, and retail. These sectors consider its integration for stronger business growth.
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is a transformative IT structure. Financial services, game makers, automotive industries, and healthcare diagnostic systems find its usage ideal. Hence, they prefer having cloud computing over other computing services.
Edge Computing
Conversely, telecom companies and middle-ware enterprises find the integration of edge computing more lucrative.
Fog Computing Vs Cloud Computing Vs Edge Computing: Which is Better?
All three, fog computing, edge computing, and cloud computing, are different computing models. They all are designed to serve different purposes. Hence, the decision to choose the one should be based on your requirements and the size and type of your business. For instance, fog computing is the best choice for those looking for real-time response applications or who want to reduce the load on the device and cloud.
At the same time, Cloud computing is best for long-term data analysis and storage. This computing model offers advanced processing and storage capabilities. Edge computing is ideal for businesses that utilize IoT as it helps with real-time response applications. Edge computing offers improved performance, reduced latency, and increased security. You can choose the one that fits your business requirements well.
Bottom Line
So, this is all about the differences between Fog computing Vs. Cloud computing Vs. Edge computing. Hopefully, this article has been informative for you and has helped you gain valuable insights that will assist you in selecting the appropriate computing system for your business needs. With the computing system, you can drive your business virtually anywhere.
All three computing systems enable employees to be more productive and more efficient. Although these services vary greatly, they all share a common goal, i.e., business growth. In this world of cut-throat competition, having the most appropriate computing system is a MUST. The right computing system allows businesses to uncover opportunities and choices that help them grow and achieve their goals.