Indeed, computing has existed for decades and has changed dramatically with the approach and technologies that have come forward to address this vast range of needs. Each of these different features, advantages, and purposes is designed to suit certain tasks and industries as the technology continues to grow, from traditional desktop computing to cloud-based systems, and then artificial intelligence and quantum computing. Each of these latest types of computing brings a new possibility.
Such developments not only mean an improvement in the way we might process information but also propel a civilization forward toward progress in industries as varied as healthcare, education, finance, and entertainment. Understanding the various types of computing and their applications does indeed help to comprehend in what respect technology has interwoven itself so deeply into the individual’s everyday life and how it continues to shape the future.
In this article, let’s have a close look at the most significant types of computing and how they apply in daily life and across fields. Whether for personal use, management of any business, or solving complex problems in science and technology, computing has now taken a central role in deciding how we live, work, and relate to our surroundings.
What is Computing?
The use of computers or other digital devices for performance, problem-solving, or even information management. It involves using programs and applications in software as well as hardware, such as computers, servers, and networks, to perform a vast array of tasks, ranging from routine numerical calculations to complex data analysis.
To make it easy, computing includes the simplest actions, such as sending emails or surfing the internet, running applications on smartphones, and more sophisticated activities like developing software and making use of machines to perform simulations, process large volumes of data, and use artificial intelligence to automate any kind of work.
Computing has become the core of modern technologies in most sectors while also becoming important for numerous industries, including education, healthcare, finance, entertainment, and many others. It helps us connect, communicate, create, and solve real-world problems very efficiently.
9 Types of Computing
Here is the list of different types of computing you should know for your business,
1. Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is one of the most popular models that is present in IT infrastructure. Users access data, applications, and services over the internet, rather than depending on local servers or individual devices. It offers scalability, flexibility, as well as cost efficiency for businesses of all sizes.
Key benefits:
- Availability of resources on demand.
- Reduce IT costs.
- Facilitates collaboration.
- Data security and backup.
Some examples of cloud computing are cloud storage services like Google Drive, Dropbox, and Amazon Web Services (AWS), which provide data storage in the cloud and power computing capability for diverse applications.
2. Grid Computing
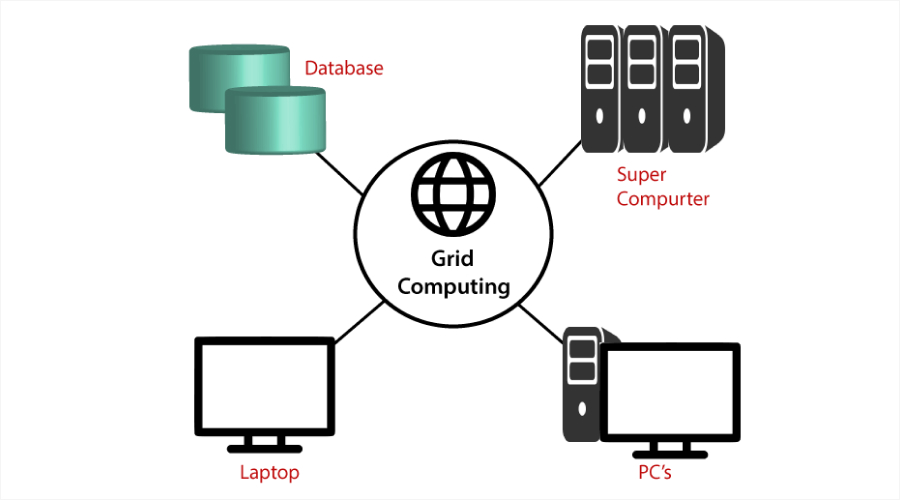
Grid computing is connecting multiple geographically distributed computers to solve one large problem, typically science or large academic projects. Grid computing may enable faster processing of complex calculations using the aggregate power of thousands of machines than could be achieved by any single computer.
Key benefits:
- Faster processing speed.
- Low-cost computing for applications that need many resources.
- Exploitation of otherwise idle resources.
Used mainly in research settings, such as climate modeling and protein folding simulations.
3. Distributed Computing
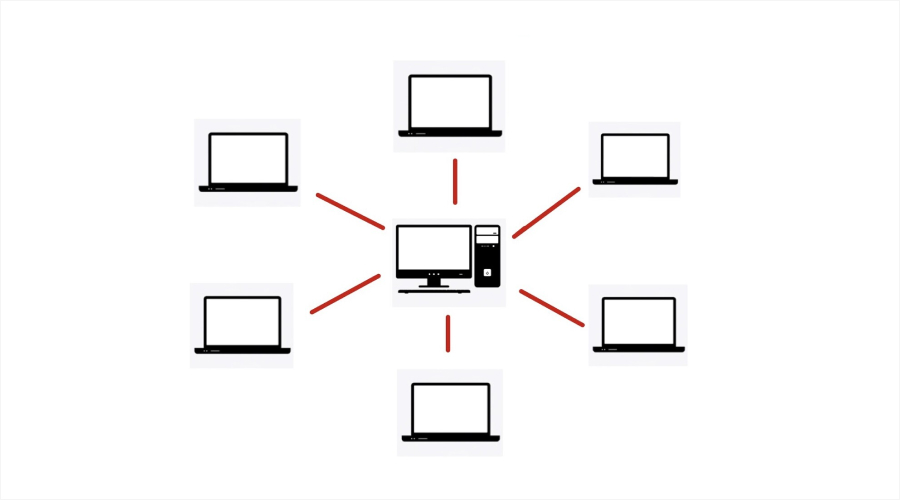
Distributed computing is the case where several computers are working on the same problem, rather like a set of rooks in a game of chess; the jobs are distributed, and then machines work on information independently. The machines are distributed geographically but coordinated in their mission to produce one outcome.
Key benefits:
- Improved performance due to parallel processing.
- Reliability through redundancy.
- Scalability for large data sets.
Many websites and online services employ distributed computing to handle enormous data sets, such as web search engines and content distribution networks (CDNs).
4. Cluster Computing
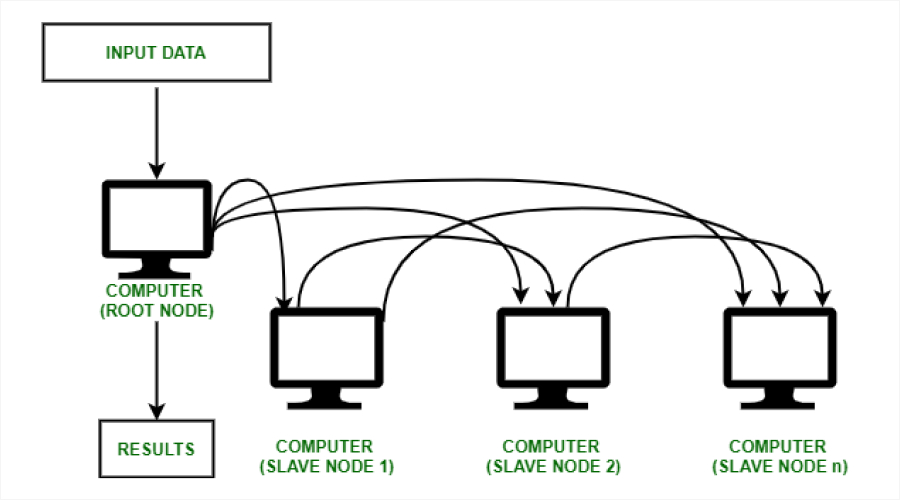
A cluster computes several computers close to each other to act as a powerful system. Cluster computing is widely used in the areas of scientific simulation, financial modeling, and business applications related to large data.
Key benefits:
- High availability.
- Enhanced processing power.
- Cost advantages over supercomputers.
Clusters are used in high-computing industries such as aerospace simulation and oil exploration.
5. Personal Computing

The type of computing that most people can identify with is personal computing—the use of a desktop, laptop, or tablet for day-to-day activities. Personal computing allows an individual to be independent to do word processing, play games, or browse the Internet without reliance on external factors.
Key benefits:
- Accessibility and usability.
- Mobile with laptops and smartphones.
- Scope of use: personal and professional.
Most technology rests based on personal computing in the form of simple office work to quite intricate creative projects.
6. Time-Sharing Computing
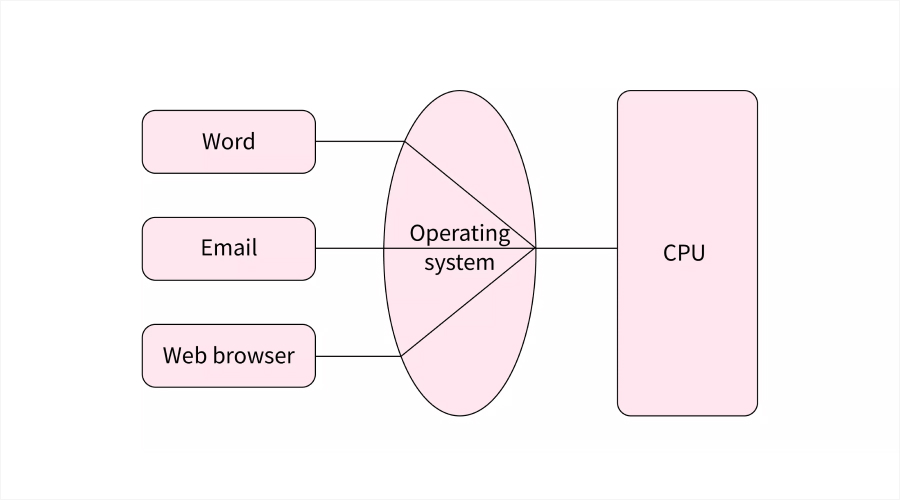
In time-sharing computing, a central system can be shared by thousands of users by dividing the processing time. Each user works on the same system, and the appearance is of having the system to oneself even though the resources are in reality shared.
Key benefits:
- Resource efficient.
- Supports many users simultaneously.
- Cost-effective in a multi-user environment.
Time-sharing was often very important in the construction of early operating systems and mainframe computers.
7. Client-Server Computing
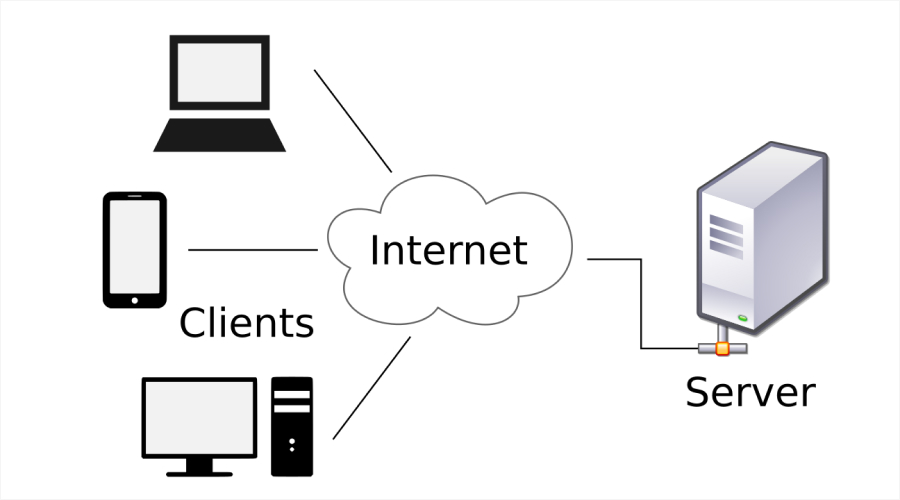
Client-server is a network configuration in which clients request services from a central server. The request is dealt with by the server, and data or services are delivered. This model is widely used in web applications, databases, and email systems.
Key benefits:
- Centralized control and security.
- Simple client system management.
- Resource management in an efficient manner.
This is the core model of the modern network, like internet services and enterprise-level applications.
8. Peer-to-Peer Computing
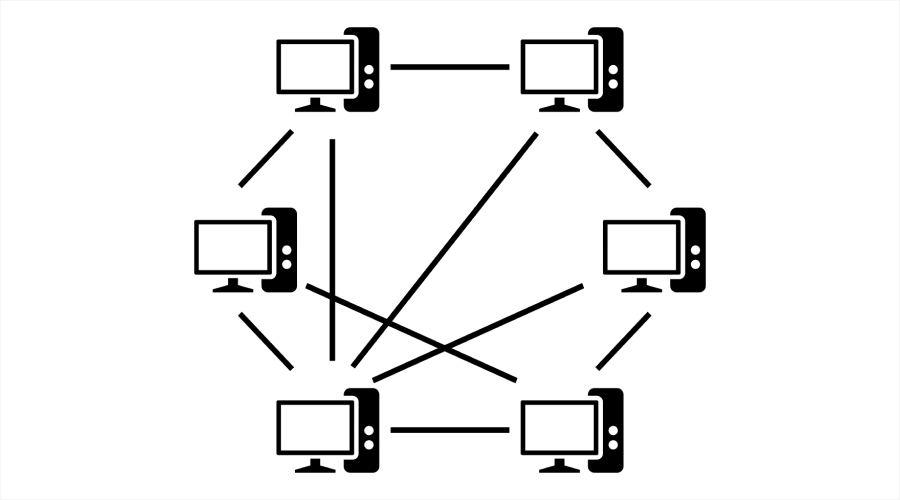
The P2P model is a setup in which devices can communicate directly with each other without the involvement of a central server. In a network, every device acts as a client as well as a server. This system shares all of its resources and data directly.
Key benefits:
- Decentralized architecture.
- It can easily work on large networks.
- It enhances the user’s privacy and anonymity.
P2P networks are also adopted typically in file-sharing applications like BitTorrent and found applications in blockchain and DeFi.
9. Mobile Computing

Mobile computing is the ability to use computing resources on portable devices, such as a smartphone, a tablet, or a laptop. Mobile computing is of paramount importance in day-to-day life. It has empowered the user to access data, communicate, and perform tasks on the go.
Key benefits:
- Portability and convenience
- Immediate access to data and applications
- Access to a wide view of applications and services
From sending messages and doing business over geographic distances using GPS maps, mobile computers offer ultimate flexibility and connectivity.
Conclusion
Each type of computing plays a role in today’s digital world. Be it client-server computing with its power centralization; grid computing marked by its collaborative nature; or lastly, mobile computing to enable flexibility, these technologies drive the applications and innovation that are upholding today’s technologies. Knowing them is in itself helpful, as it enlightens what otherwise is a confusing technological landmass that will define our future.