What is Robotic Process Automation (RPA)?
RPA stands for Robotic Process Automation. It is a technology that enables software robots, or “bots,” to automate routine and repetitive tasks that are typically performed by humans. These bots can be programmed to mimic the actions of a human user and interact with various applications, systems, and data sources.
Robotic process automation bots are designed to perform structured tasks, such as data entry, form filling, and document processing. They can be used to automate a wide range of business processes, such as customer service, finance and accounting, human resources, and supply chain management.
RPA technology is typically used to improve the efficiency, accuracy, and speed of business processes, while reducing costs and freeing up human workers to focus on more strategic tasks. It can be particularly useful for organizations that have high-volume, repetitive tasks that are prone to errors or require significant amounts of time and resources.
RPA technology is often used in conjunction with other automation technologies, such as Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML), to enable more sophisticated and intelligent automation solutions. Overall, robotic process automation has the potential to transform the way organizations operate and deliver value to their customers.
Related Article: RPA vs AI: Understanding the Differences and Benefits
Why is Robotic Process Automation (RPA) Important?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a technological advancement that leverages software bots to automate repetitive mundane tasks. RPA has become increasingly important in the modern business world due to its potential to transform labor-intensive processes, increasing efficiency and productivity. RPA development services is proving to be a game-changer for organizations across industries as it offers an array of benefits that help businesses save time, money, and resources.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is important for several reasons:
Efficiency: RPA can automate routine, repetitive, and time-consuming tasks, allowing organizations to complete them more quickly and efficiently. This can free up employees to focus on higher-value work that requires human skills and expertise.
Accuracy: RPA can help improve the accuracy and consistency of work performed by eliminating human errors, such as data entry mistakes or calculation errors.
Scalability: Robotic process automation can scale up or down quickly based on the organization’s needs, allowing it to adapt to changing business requirements or customer demands.
Compliance: RPA can help organizations comply with regulatory requirements by ensuring that tasks are completed consistently and accurately.
Customer Satisfaction: RPA can help improve customer satisfaction by enabling faster response times and reducing errors in customer-facing processes such as order processing or claims management.
Overall, robotic process automation has the potential to transform the way organizations operate by improving efficiency, accuracy, and customer satisfaction while reducing costs and freeing up employees to focus on higher-value work.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) Life Cycle Stages?
The robotic process automation life cycle typically consists of the following stages:
Discovery: In this stage, organizations identify the processes that are best suited for automation. They analyze their existing workflows and identify opportunities for automation, such as repetitive, rule-based tasks.
Design: In this stage, organizations design the automation solution. This includes identifying the processes to be automated, designing the workflow, and selecting the RPA tool or tools to be used.
Development: In this stage, the automation solution is developed. This includes creating the bot, developing the scripts, and integrating the bot with the target system.
Testing: In this stage, the automation solution is tested to ensure that it performs as expected. This includes testing the bot’s functionality, accuracy, and performance.
Deployment: In this stage, the automation solution is deployed into production. This includes setting up the environment, installing the bot, and training the users.
Operations and Maintenance: In this stage, the automation solution is monitored and maintained. This includes tracking the bot’s performance, identifying and resolving issues, and updating the solution as needed.
Continuous Improvement: In this stage, organizations continuously improve the automation solution. This includes identifying new opportunities for automation, optimizing the bot’s performance, and incorporating feedback from users.
Overall, this life cycle is a continuous process that involves identifying opportunities for automation, designing and developing the solution, testing and deploying it, and then continuously monitoring and improving it over time.
RELATED: What is DevOps Automation: Best Practices and Benefits
Advantages of RPA
There are several advantages of using RPA:
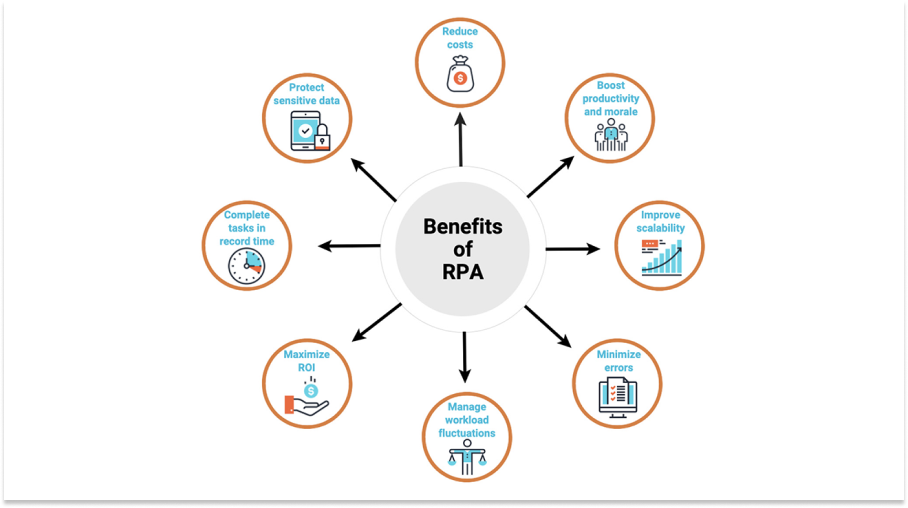
Improved Efficiency: Can automate repetitive and mundane tasks, allowing employees to focus on more important and strategic work. This can help organizations improve their efficiency and productivity.
Increased Accuracy: Can reduce the likelihood of errors, as bots are programmed to follow specific rules and perform tasks consistently. This can help improve the accuracy of data entry, processing, and analysis.
Cost Savings: Can help reduce labor costs by automating tasks that would otherwise require human workers. This can also help organizations save money by reducing errors and improving productivity.
Faster Processing Time: Can complete tasks faster than humans, as bots are not subject to fatigue or human error. This can help organizations improve their response times and meet customer expectations.
Scalability: Can scale up or down quickly based on an organization’s needs, allowing it to adapt to changing business requirements or customer demands.
Improved Compliance: Can help ensure compliance with regulations and industry standards by ensuring that tasks are completed consistently and accurately.
Enhanced Customer Experience: Can improve the customer experience by enabling faster response times, reducing errors in customer-facing processes, and freeing up employees to focus on higher-value work.
Overall, Can help organizations improve their efficiency, accuracy, and productivity while reducing costs and improving customer satisfaction.
Disadvantages of RPA
Despite its benefits, RPA also has some potential disadvantages:
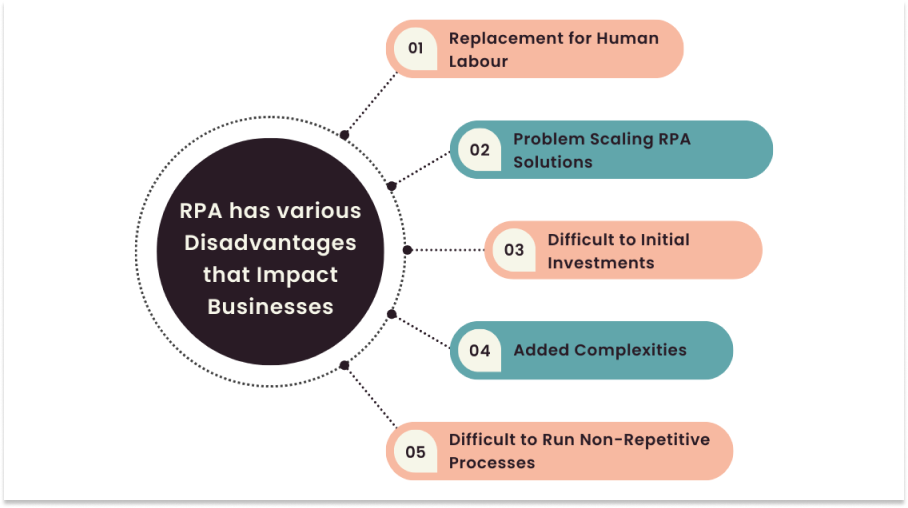
Limited Ability to Handle Unstructured Data: It is designed to work with structured data that can be easily processed by bots. It may struggle to handle unstructured data, such as handwritten documents or non-standardized data formats.
High Upfront Costs: Implementing It can involve significant upfront costs, including licensing fees, infrastructure costs, and development costs. This can be a barrier for some organizations, especially smaller ones.
Difficulty with Complex Tasks: It is best suited for automating routine and repetitive tasks. It may struggle with more complex tasks that require human judgment, decision-making, or problem-solving skills.
Risk of Job Losses: It can potentially automate jobs that were previously performed by humans, leading to job losses or displacement. This can create resistance to the adoption of RPA, especially from employees who fear losing their jobs.
Conclusion
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) life cycle is an important concept to understand when it comes to automation and robotics. Its six distinct stages can help professionals plan, develop, implement, monitor and maintain robotic processes. The successful completion of each stage in the robotic process automation life cycle leads to stronger and more efficient operations. Knowing the different elements of the RPA life cycle will help companies achieve their desired outcomes with greater efficiency and faster results.
Author Bio: Hi, I am Sai Thirumal, working as a Research Analyst and interested in writing a wide range of tech blogs, and articles. I am fond of writing tech articles on Machine Learning, AWS, DevOps, Tosca Certification and other latest technologies. Also, interested in doing in-depth research on various technology updates and putting them in writing and sharing.